Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, NOS. Clinicopathological study in a cohort of peruvian patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37711/rpcs.2020.2.3.191Keywords:
Herpesvirus 4 Human, Germinal Center, Peru, Epstein-Barr Virus Infec-tions, Cohort Studies, Lymphoma, B-Cell, Stomach, Biomarkers, Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-BCL-2Abstract
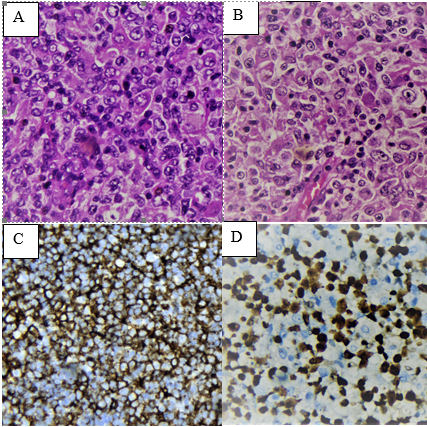
Objective. To evaluate the clinicopathological characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (LCBGD, NOS), in a cohort of peruvian patients. Methods. Seventy-two cases with a diagnosis of LCBGD, NOS, were studied at the INEN. Clinicopathological characteristics, overall survival (OS) and other clinical parameters were evaluated according to origin cell, Epstein-Barr virus infection (EBER), and the immunohistochemical expression (IHC) of MYC and BCL2. Results. There were 54% women and 46% men, with an average age of 65 years. 76% were ganglionic, the majority cervical location and 24% extranodal, the stomach being the most affected. The most frequent stages were II (35%) and III (29%), the majority with medium-high and high IPI. Histologically, almost all cases had centroblastic and immunoblastic morphology. There was a similar proportion of cases with germinal center (GCB) and non-germinal center (non-GCB) subtypes. GCB and EBER+ had better OS than non-GCB and EBER-, respectively. Likewise, cases with negative IHC for MYC and BCL2 had better OS and a higher percentage in early stages. These findings were not statistically significant. Conclusion.Our cases show characteristics similar to those described in the literature, although with a higher percentage associated with EBV and non-GCB cases. The small number of cases evaluated with IHC to determine subtypes and biomarkers may have limited the statistical analysis in this cohort of cases.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Revista Peruana de Ciencias de la Salud

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.