Multidisciplinary approach to X-linked hypophosphatemia: A literature review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37711/rpcs.2024.6.4.551Keywords:
genotype-phenotype analysis, outcome evaluation, X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets, healthAbstract
X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is the most common hereditary form of rickets and osteomalacia. It results from dysregulated fbroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) due to a mutation in the PHEX gene, leading to decreased tubular phosphate reabsorption, reduced renal 1a-hydroxylase activity, and increased renal 24-hydroxylase activity. Patients with XLH present with rickets and osteomalacia, severe lower limb deformities, bone and muscle pain, growth retardation, and reduced quality of life. As a multisystemic disorder, XLH requires a multidisciplinary approach involving highly specialized felds. Severe complications associated
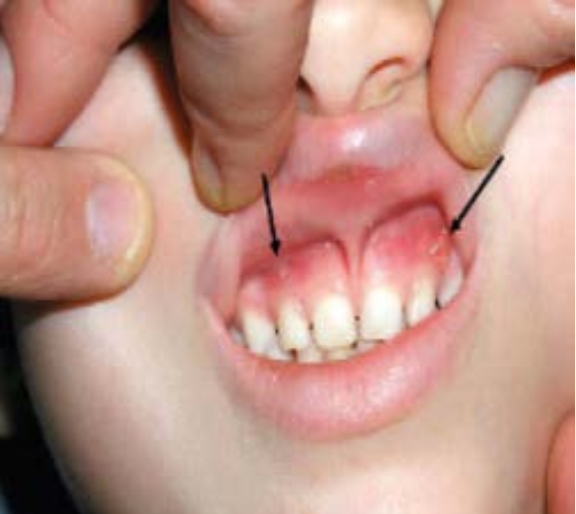
with XLH include craniosynostosis, hearing loss, progressive bone deformities, recurrent dental
and periodontal lesions, and psychosocial distress. Given these concerns, we conducted a literature review of PLOS ONE and the PubMed and Google Scholar databases, focusing on publications from the past fve years, to refne diagnostic and treatment approaches.
Downloads
References
Hawley, S., Shaw, N. J., Delmestri, A., Prieto-Alhambra, D., Cooper, C., Pinedo-Villanueva, R., ... & al. (2020). Prevalence and Mortality of Individuals With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: A United Kingdom Real-World Data Analysis. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 105(3), e871–e880. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgz203
Emma, F., Cappa, M., Antoniazzi, F., Bianchi, M. L., Chiodini, I., Eller-Vainicher, C., ... & al. (2019). X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: an Italian experts’ opinion survey. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 45(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-019-0654-6
Beck-Nielsen, S. S., Mughal, Z., Haffner, D., Nilsson, O., Levtchenko, E., Ariceta, G., ... & Mäkitie, O. (2019). FGF23 and its role in X-linked hypophosphatemia-related morbidity. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 14(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1014-8
Mindler, G. T., Kranzl, A., Stauffer, A., Haeusler, G., & Raimann, A. (2020). Disease-specific gait deviations in pediatric patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia. Gait & Posture, 81, 78-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2020.07.007
Haffner, D., Emma, F., Eastwood, D. M., Duplan, M. B., Bacchetta, J., Schnabel, D., ... & al. (2019). Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of X-linked hypophosphataemia. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 15(7), 435-455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0152-5
Linglart, A., Imel, E. A., Whyte, M. P., Portale, A. A., Högler, W., Boot, A. M., ... & al. (2022). Sustained Efficacy and Safety of Burosumab, a Monoclonal Antibody to FGF23, in Children With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 107(3), 813-824. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgab729
Imel, E. A. (2021). Burosumab for Pediatric X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Current Osteoporosis Reports, 19(3), 271-277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-021-00669-9
Park, P. G., Lim, S. H., Lee, H., Ahn, Y. H., Cheong, H. I., & Kang, H. G. (2021). Genotype and Phenotype Analysis in X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 9, 699767. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.699767
Baroncelli, G. I., & Mora, S. (2021). X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets: Multisystemic Disorder in Children Requiring Multidisciplinary Management. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 12, 688309. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.688309
Baroncelli, G. I., Zampollo, E., Manca, M., Toschi, B., Bertelloni, S., Michelucci, A., ... & al. (2021). Pulp Chamber Features, Prevalence of Abscesses, Disease Severity, and PHEX Mutation in X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets. Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism, 39, 212–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-020-01136-8
Scorcelletti, M., Kara, S., Zange, J., Jordan, J., Semler, O., Schönau, E., ... & al. (2022). Lower limb bone geometry in adult individuals with X-linked hypophosphatemia: an observational study. Osteoporosis International, 33(7), 1601-1611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-022-06385-z
Schindeler, A., Biggin, A., & Munns, C. F. (2020). Clinical Evidence for the Benefits of Burosumab Therapy for X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) and Other Conditions in Adults and Children. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 11, 338. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00338
Takase, R., Nakano, Y., Hasegawa, K., & Otsuka, F. (2020). X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) Mimicking Rheumatic Disease. Internal Medicine, 59(9), 1233-1234. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.4029-19
Ward, L. M., Glorieux, F. H., Whyte, M. P., Munns, C. F., Portale, A. A., Högler, W., ... & al. (2022). Effect of Burosumab Compared with Conventional Therapy on Younger vs Older Children With X-linked Hypophosphatemia. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 107(8), e3241-e3253. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgac296
Glorieux, F. H., Bonewald, L. F., Harvey, N. C., & van der Meulen, M. C. H. (2022). Potential influences on optimizing long-term musculoskeletal health in children and adolescents with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 17(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-021-02156-x
Martel-Villagrán, J., Arias-Medina, A., & García-Mardones, G. (2020). Usefulness of X-rays in the Differential Diagnosis of Hypophosphataemic Rickets. Advances in Therapy, 37(2), 89-94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-01183-2
Dahir, K., Roberts, M. S., Krolczyk, S., & Simmons, J. H. (2021). X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: A New Era in Management. Journal of the Endocrine Society, 5(5), bvab054. https://doi.org/10.1210/jendso/bvaa151
Rothenbuhler, A., Schnabel, D., Högler, W., & Linglart, A. (2020). Diagnosis, treatment-monitoring and follow-up of children and adolescents with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). Metabolism, 103S, 153892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2019.03.009
Romagnoli, C., Iantomasi, T., & Brandi, M. L. (2022). Impact of X-Linked Hypophosphatemia on Muscle Symptoms. Genes (Basel), 13(12), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122415
Beck-Nielsen, S. S., Mughal, Z., Haffner, D., Nilsson, O., Levtchenko, E., Ariceta, G., ... & Mäkitie, O. (2019). FGF23 and its role in X-linked hypophosphatemia-related morbidity. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 14(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1014-8
Vincze, J., Skinner, B. W., Tucker, K. A., Conaway, K. A., Lowery, J. W., & Hum, J. M. (2021). The Metabolic Bone Disease X-linked Hypophosphatemia: Case Presentation, Pathophysiology and Pharmacology. Life (Basel), 11(6), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060563
González-Lamuño, D., Lorente Rodríguez, A., Luis Yanes, M. I., Marín-Del Barrio, S., Martínez Díaz-Guerra, G., & Peris, P. (2022). Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of X-linked hypophosphatemia: A consensus based on the ADAPTE method. Medicina Clínica (Barcelona), 159(3), 152.e1-152.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2021.07.029
Vakharia, J. D., Matlock, K., Taylor, H. O., Backeljauw, P. F., & Topor, L. S. (2018). Craniosynostosis as the Presenting Feature of X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets. Pediatrics, 141(5), S515-S519. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-2522
Lafage-Proust, M. H. (2022). What are the benefits of the anti-FGF23 antibody burosumab on the manifestations of X-linked hypophosphatemia in adults in comparison with conventional therapy? A review. Therapeutic Advances in Rare Disease, 3, 26330040221074702. https://doi.org/10.1177/26330040221074702
DeLacey, S., Liu, Z., Broyles, A., El-Azab, S. A., Guandique, C. F., James, B. C., & Imel, E. A. (2019). Hyperparathyroidism and parathyroidectomy in X-linked hypophosphatemia patients. Bone, 127, 386-392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2019.06.025
Brener, R., Zeitlin, L., Lebenthal, Y., & Brener, A. (2022). Dental health of pediatric patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) after three years of burosumab therapy. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 13, 947814. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.947814
Munns, C. F., Maguire, E. P., Williams, A., Wood, S., & Biggin, A. (2023). Craniosynostosis in Patients With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: A Review. JBMR Plus, 7(5), e10728. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm4.10728
Sarafrazi, S., Daugherty, S. C., Miller, N., Boada, P., Carpenter, T. O., Chunn, L., ... & al. (2022). Novel PHEX gene locus-specific database: Comprehensive characterization of vast number of variants associated with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). Human Mutation, 43(2), 143-157. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.24296
Vakharia, J. D., Matlock, K., Taylor, H. O., Backeljauw, P. F., & Swartz Topor, L. (2018). Craniosynostosis as the Present Feature of X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets. Pediatrics, 141(e20172522). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-2522
Fuente, R., García-Bengoa, M., Fernández-Iglesias, Á., Gil-Peña, H., Santos, F., & López, J. M. (2022). Cellular and Molecular Alterations Underlying Abnormal Bone Growth in X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020934
Hamdy, N. A. T., Harvengt, P., & Usardi, A. (2021). X-linked hypophosphatemia: The medical expert’s challenges and the patient’s concerns on their journey with the disease. Archives de Pédiatrie, 28(7), 612-618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcped.2021.09.005
Imel, E. A., & White, K. E. (2019). Pharmacological management of X-linked hypophosphataemia. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 85(6), 1188-1198. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13763
Padidela, R., Whyte, M. P., Glorieux, F. H., Munns, C. F., Ward, L. M., Nilsson, O., ... & al. (2021). Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Randomized, Active-Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial of Burosumab Versus Conventional Therapy in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Calcified Tissue International, 108(5), 622-633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-020-00797-x
Padidela, R., Nilsson, O., Makitie, O., Beck-Nielsen, S., Ariceta, G., Schnabel, D., ... & al. (2020). The international X-linked hypophosphataemia (XLH) registry (NCT03193476): rationale for and description of an international, observational study. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 15(1), 172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-020-01434-4
Seefried, L., Smyth, M., Keen, R., & Harvengt, P. (2021). Burden of disease associated with X-linked hypophosphataemia in adults: a systematic literature review. Osteoporosis International, 32, 7–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-020-05548-0
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Britto Ebert Falcon-Guerrero, Guido Sebastián Falcón-Pasapera, Robert Willy Falcón-Guerrero

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.