Efficacy test of a solar concentrator for water disinfection for human consumption
Keywords:
design, concentrator, human consumption water, mi-croorganisms, thermicAbstract
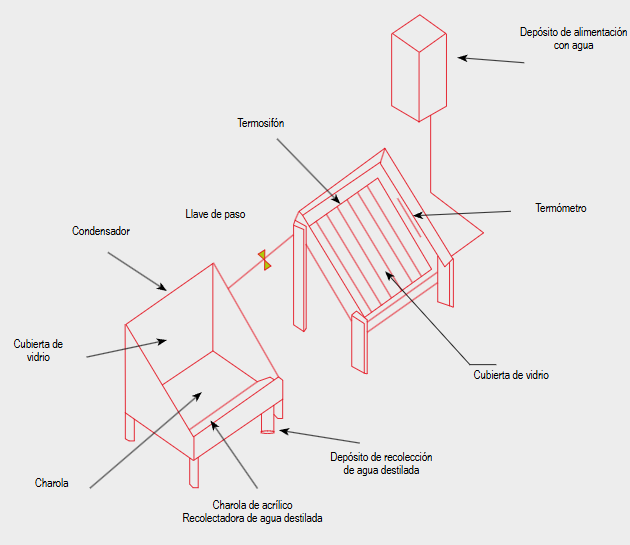
Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness of the solar concentrator for disinfection of water for human consumption in the Casha population center (C.P.), Huanuco, Peru. Methods. The study was inductive-analytic, analytical and longitudinal, with a quasi-experimental design and a quantitative approach. The sample population consisted of 15 households in the Casha sector. The hypothesis test was performed using Student's t-test. Results. Evaluation of bacteriological parameters revealed that the standard error for total coliforms was 1.155 and the t-test showed a statistically significant value of t = 3.464, p = 0.004. This indicates that the null hypothesis is rejected, confirming that solar concentrators have the ability to effectively remove total coliforms, improving the quality of water for human consumption. For thermotolerant coliforms, the standard error was 1.195, with a statistically significant value of t = 5.464, p = 0.009. For heterotrophic bacteria, the standard error was 1.104, and the t-test indicated t = 5.464, p = 0.009. These results demonstrate that the solar concentrator is effective in reducing microorganisms (total coliform, thermotolerant and heterotrophic bacteria) present in the water. Conclusions. The analyses confirmed that the solar concentrator was able to effectively eliminate microorganisms (total coliform, thermotolerant and heterotrophic bacteria), thus validating that the solar concentrator is an effective solution to ensure that water is safe and suitable for human consumption
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Milton Edwin Morales Aquino (Autor/a)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


