Design of a health monitoring system for astronauts based on artifcial intelligence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37711/idac.2024.1.2.4Keywords:
health monitoring, artifcial intelligence, astronaut, biosignals, neuronal networks, biomedical sensors, space healthAbstract
Objective. To design a health monitoring system for astronauts through the integration of the artifcial intelligence (AI) and biomedical sensors. Methods. A experimental type study was developed. The population consisted of simulated data of
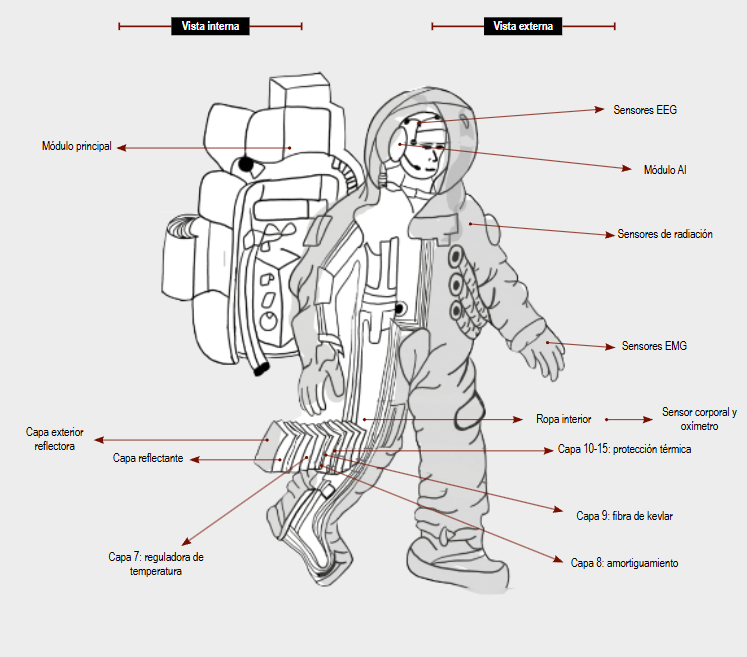
astronauts and the sample was obtained through the intentioned selection of critical biometric parameters. The data was collected using a set of sensors EEG, EMG, and optics, integrated in a smart suit. The signals were processed in real time through a central module with technology ESP32 and the use of neural networks RNN-CNN for the analysis were proposed. Results. An AI architecture is proposed that, theoretically, it could achieve 90% accuracy in detecting potential diseases. The system presented a data transmission rate of 1.5 kbps and a latency of < 100 ms, which would allow real-time monitoring. Conclusions. The system developed has the potential to be effective for the early detection of alterations in the health of astronauts, showing its capacity for safeguarding the safety of space missions.
Downloads
References
Boulemtafes, A., Khemissa, H., Derki, M. S., Amira, A., & Djedjig, N. (2021). Deep learning in pervasive health monitoring, design goals, applications, and architectures: An overview and a brief synthesis. Smart Health, 22, 100221.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smhl.2021.100221
Corpas Novo, J. A. (2019). Aceleración y optimizacion del consumo energetico de clasifcadores en cascada para la deteccion de rostros sobre arquitecturas asimétricas [Tesis doctoral, Universidad de Granada]. Repositorio UG. https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/56822/81404.pdf?sequence=4&isAllowed=y
Di Rienzo, M., & Piccirillo, S. G. M. (2021). Wearables for life in space. Wearable Sensors. 463-486. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818475-6.00001-8
Lipková, J., Chen, R. J., Chen, B., Lu, M., Barbieri, M., Shao, D., Vaidya, A., Chen, C., Zhuang, L., Williamson, D. F. K., Shaban, M., Chen, T., & Mahmood, F. (2022). Artificial intelligence for multimodal data integration in oncology. Cancer Cell, 40(10), 1095-1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.09.012
Martin, A. S., & Freeland, S. (2021). The advent of artifcial intelligence in space activities: New legal challenges. Space Policy, 55, 101408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spacepol.2021.101408
Roda, A., Mirasoli, M., Guardigli, M., Zangheri, M., Caliceti, C., Calabria, D., & Simoni, P. (2018). Advanced biosensors for monitoring astronauts’ health during long-duration space missions. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 111, 18-26.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.012
Roslee, M. F. (2021). Review of medical capabilities requirements for manned missions on lunar and Martian surfaces base activities. REACH, 23-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reach.2020.100042
Salvi, M., Loh, H. W., Seoni, S., Barua, P. D., Del Barrio-García, S., Molinari, F., & Acharya, U. R. (2023). Multi-modality approaches for medical support systems: A systematic review of the last decade. Information Fusion, 102134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102134
Shaik, T., Tao, X., Li, L., Xie, H., & Velásquez, J. D. (2024). A survey of multimodal information fusion for smart healthcare: Mapping the journey from data to wisdom. Information Fusion, 102, 102040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102040
Solís García, E. (2017). Utilización del programa Face2Gene en diferentes escenarios clínicos [Tesis de grado, Universidad de Cantabria]. Repositorio institucional de la Universidad de Cantabria. https://repositorio.unican.es/xmlui/handle/10902/11747
Sujith, A. V. L. N., Sajja, G. S., Mahalakshmi, V., Nuhmani, S., & Balaji, P. (2022). Systematic review of smart health monitoring using deep learning and artificial intelligence. Neuroscience Informatics, 2(3), 100028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuri.2022.100028
Tipaldi, M., Feruglio, L., Denis, P., & D’Angelo, G. (2020). On applying AI-driven flight data analysis for operational spacecraft model-based diagnostics. Annual Reviews in Control, 49, 197-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.01.001
Vandendriessche, B., Godfrey, A., & Izmailova, E. S. (2021). Multimodal biometric monitoring technologies drive the development of clinical assessments in the home environment. Maturitas, 151, 41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.06.009
Villanueva Alarcón, R. A. (2021). Sistema inteligente basado en redes neuronales para la identifcación de cáncer de piel de tipo melanoma en imágenes de lesiones cutáneas [Tesis de grado, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos]. Cybertesis Repositorio UNMSM. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12672/17574
Zangheri, M., Mirasoli, M., Guardigli, M., Di Nardo, F., Anfossi, L., Baggiani, C., Simoni, P., Benassai, M., & Roda, A. (2019). Chemiluminescence-based biosensor for monitoring astronauts’ health status during space missions: Results from the International Space Station. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 129, 260-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.034
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rivaldo Carlos Duran Aquino, Nataly Andrea Rojas Barnett, Hanks Jeremy Reyes Huaman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.